Guidehouse
Mackinnon Lawrence is a director in the Guidehouse global Energy practice and leads Guidehouse Insights. He is responsible for overall strategy and operations, including management of a global analyst team, development of the Firm’s Energy Cloud thought leadership framework, and client engagements supporting utility, oil & gas, telecom, manufacturing, IT, and consumer tech companies. His expertise covers energy transformation, business model innovation, and technology disruption.
Richelle Elberg is an associate director at Guidehouse. Her primary focus is on utility communications networks for AMI and distribution/substation automation applications. Elberg has more than twenty years of experience in the telecommunications industry, including an extensive background analyzing and writing on the wired and wireless communications industries from operational, financial, strategic, technical, and regulatory perspectives.
Utilities today, along with the people living and working in the communities they serve, face myriad evolving threats and challenges. In the midst of the ongoing energy transition — wherein new industrial norms such as digitalization, automation, and electrification are being adopted — utilities must keep the lights on while simultaneously upgrading sometimes century-old infrastructure and integrating distributed energy resources (DER). Add rising costs and an uncertain economic outlook, ongoing supply chain bottlenecks, increasing storm intensity, and new Environmental, Social, and Corporate Governance mandates to the picture, and the depth and breadth of power industry challenges is clear.
While the future remains uncertain, based on Guidehouse's ninth annual survey of industry stakeholders, in partnership with Public Utilities Fortnightly, utilities are embracing the opportunity to redefine resilience and improve the lived experience of their customers. The power grid is foundational to a thriving community, and utilities understand the critical role they play in helping constituents weather climate change impacts, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, integrating sustainable renewables into the power generation mix, and electrifying building and transportation infrastructure, all with the goal of a more resilient, sustainable grid.
Increasingly, the utilities industry's role in supporting social equity is also prioritized, as can be seen in recent legislation such as the green energy-focused U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), which provides enhanced benefits for investments made in lower-income communities. Below, we explore how utility sentiment is evolving across four key energy transition themes.
Technology Advances Support Industry Goals
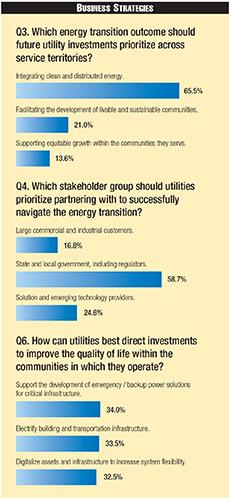
According to survey responses, technological advances for meeting energy transition demands are keeping pace with transformation and utilities recognize the need to accelerate integration. When asked what energy transition outcome should be prioritized within their territories, a majority of survey respondents (64.5%) pointed to integration of clean and distributed energy.
A growing number (21%) suggested that facilitating the development of livable, sustainable communities to meet broader resilience goals must be top-of-mind. Nearly 14% prioritized supporting equitable community growth, another sign that social equity is gaining mindshare as an important outcome, but lags as a priority issue for utilities within the energy transition.
 Disruptions
Disruptions
The focus on clean and distributed energy coincides with a wave of emerging technology deployment across the industry. Utilities are upgrading to second-generation smart meters. Guidehouse Insights estimates that more than 8.5 million will be installed by year-end.
They are embracing more robust networking protocols for increased grid visibility and control, and implementing an enhanced, 360-degree view of the customer solutions. EV-charging infrastructure is proliferating at an accelerating pace. Guidehouse Insights forecasts a tenfold-plus increase in charging points across North America by 2031, when more than fifty million locations are forecast, up from fewer than five million today.
Battery storage continues to ride an accelerating wave of demand to optimize intermittent generation from wind and solar. Clean hydrogen is increasingly central to decarbonization strategies and drones are increasingly used to inspect power lines, reduce costs, and improve network visibility.
Finally, cybersecurity efforts have ramped up markedly in recent years. Indeed, the cyber threat was considered the greatest risk to utilities in 2022's State and Future survey and utilities are no longer just "checking the box" when it comes to cybersecurity.
Power Industry Embraces Leadership Role, Struggles Under Restrictive Regulatory Constructs
 Challenges
Challenges
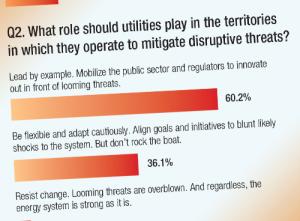
Utilities have embraced the changing world in which they operate and are making the investments to achieve their goals, but challenges remain. Most survey respondents feel the industry should take the lead in driving change to mitigate disruptive threats. In fact, more than 60% agreed that the industry should push public sector officials and regulators to innovate ahead of looming threats.
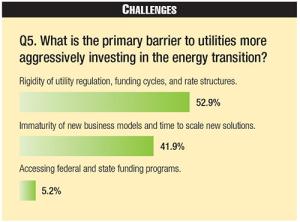
Indeed, the restrictive environment in which most North American utilities operate is seen as the industry's biggest hurdle in terms of meeting its goals and investing more aggressively in the energy transition. Fifty-three percent of respondents cited regulatory challenges as the biggest hurdle, followed by 42% who said the immaturity of new business models and the time to scale new solutions prevented more aggressive investments.
Building on the notion that restrictive regulation impedes progress, nearly 60% of survey respondents felt that state and local governments and regulators should be prioritized as partners in navigating the energy transition. Solution and emerging tech providers and large corporations were seen as less of a priority.
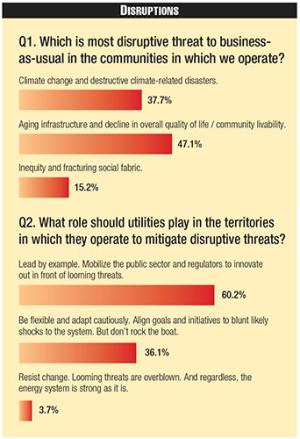
For the first time in this year's survey, respondents were asked what the most disruptive threat was to business-as-usual in the communities in which they operate, as opposed to their business. Aging infrastructure and a decline in the overall quality of life were most often cited, followed closely by climate change and related disasters. Of course, the two are interrelated: aging infrastructure is less resilient and less able to withstand growing challenges, such as flooding, fires, and the high winds seen in more violent hurricanes, and extended power outages, due either to failing equipment or storms, can have outsized negative impacts on quality of life.
 Business Strategies
Business Strategies
The digitalization of infrastructure can help. In Smart Cities, for example, Guidehouse Insights estimates that investment in predictive AI leveraging municipal data will increase nearly tenfold by 2032, becoming a $6.5 billion market. Use cases include reducing traffic pollution and congestion and helping cities better understand and conserve energy and water resources.
Mixed Views on IRA and BBB Impact, Transportation Electrification Most Cited
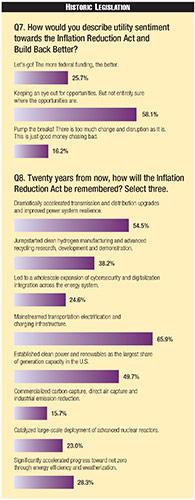
When asked about the long-term impact of the historic IRA, passed in August 2022, and the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), the bills' impact on electrifying the transportation sector was most often selected (66%), followed by anticipation of a dramatic acceleration in upgrades to the transmission and distribution (T&D) grid and improved resilience (54.5%).
Notably, the impact on EV adoption due to IRA is not expected to be immediate, as the domestic materials requirements have meant that fewer EVs on the market today are eligible for rebates than under previous rules. Still, according to Guidehouse Insights data, plug-in electric vehicle (PEV) sales more than doubled in 2021 and rose another 50% in 2022.
PEVs accounted for more than 5% of total light duty vehicle sales last year; this level has proven to be a key inflection point for adoption in countries with higher EV penetration. Twenty years out, survey respondents believe the IRA/IIJA's most memorable impact will be the mainstreaming of electrified transportation and charging infrastructure.
 Historic Legislation
Historic Legislation
Focusing on grid modernization, following passage of the IIJA and IRA, the U.S. will be investing billions of dollars toward replacing fossil fuels with low-carbon and zero-emissions alternatives, and building out the transmission and distribution system required to get clean power to where it is needed. The IIJA appropriated nearly $5 billion specifically for transmission expansion, a relatively small investment considering that Guidehouse Insights data indicates that nearly $3.9 billion in new transmission projects are being added each year.
The IRA provides another $7 billion-plus in funding for transmission upgrades and, overall, Guidehouse Insights expects a significant increase in T&D investment, although funding gaps remain, and it may not be enough to meet all goals.
Twenty years out, nearly half of all survey respondents expect clean renewable generation sources to be well-established, and, finally, clean hydrogen solutions are projected to have been given an important boost toward commercialization due to IRA.
When asked about their attitude toward the IRA and the 2021 Build Back Better Act, survey respondents were measured in their enthusiasm. More than 58% said they are keeping an eye out for opportunities but admit there is confusion around where the best opportunities are. More than a quarter of respondents fully embrace the legislative support, but 16% disagreed, saying these bills are throwing "good money after bad."
No Consensus on How to Improve Quality of Life
While survey responses overall indicate growing industry appreciation for the role utilities play in social equity and community quality of life, there remains no consensus on what direct investments utilities can make to achieve these goals. Roughly one-third each said development of backup power solutions, building/transportation electrification, or digitalization for improved grid flexibility represented the best path forward. In reality of course, all three must be achieved to support longer-term goals, as the even split among respondents implies.
More than ever before, the utilities that operate the grid, their regulators, and society at large, understand their fates should be increasingly intertwined going forward. Climate change and GHG reduction mandates make DER integration a necessity, along with building and transportation electrification.
But the resultant changing nature of power loads and flow means that Industry 4.0 technologies — automation, sensing and measurement, systems, cybersecurity — must be implemented. And the increasingly competitive environment — as opposed to the virtual monopoly utilities enjoyed for more than a century — means they must dramatically improve their customer engagement capabilities.
It won't be easy, nor happen quickly, but all these advances have the potential to drive increased quality of life and improve social equity. As we said upfront: The power grid and the utilities that enable it are foundational elements to a successful society and resilient economy. And based on this pulse survey, it appears the industry stands ready to meet the challenge.


