Transmission
NERC Today and Tomorrow
Living in the new world of mandatory reliability standards.
Mandatory reliability standards put in place by NERC three years ago give reason for optimism concerning their success. But the organization struggles with standards development, compliance, enforcement and transparency.
Taking Green Private
How merchant funding is remaking the rules for renewables.
Six weeks ago, FERC opened a notice of inquiry to invite industry comments on whether wind, solar, and other intermittent energy sources face unfair obstacles in wholesale power markets. Now assigned their own acronym—VERs, for “variable energy resources”—renewables make up a growing percentage of the nation’s energy supply portfolio. But as FERC notes, they present “unique challenges,” especially in terms of constraints on location and limits on the degree to which system operators can control or dispatch individual VER units. Thus, FERC suggests that certain common rules and practices, such as those for unit commitment, dispatch, and scheduling, might make it overly difficult to integrate VERs into the grid.
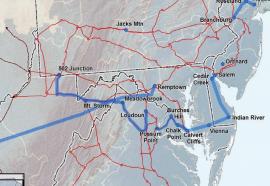
Tomorrow's T&D
The most economical energy savings might be found in grid efficiency.
Power delivery efficiency gains constitute a valuable utility asset that can offset or defer new generation and T&D investments. Enabling technologies, utility demonstration projects and supporting regulatory frameworks are needed to validate potential savings.
Outsmarting the Grid
A trio of eager tech startups confronts an industry intent on preserving the status quo.
In light of all the excitement created by smart-grid regulatory initiatives and stimulus funding, three clever tech startups have come forward with proposals for novel grid projects. In California, Western Grid Development proposes to install energy storage devices ranging in size from 10 to 50 MW at various discrete and strategic locations in PG&E’s service territory where the California ISO has identified reliability problems. Second, a company called Primary Power proposes to deploy a total of four advanced, 500-MVAR static VAR compensators (SVC) at three separate locations within the PJM footprint. Third, in Clovis, N.M., Tres Amigas plans to allow power producers to move market-relevant quantities of electric power and energy between and among the nation’s three asynchronous transmission grids: ERCOT and the Eastern and Western Interconnections.
Wellinghoff's War
FERC fights for the green-grid superhighway—even if Congress won’t.
The Senate’s deadlock over carbon cap-and-trade legislation has not deterred FERC Chairman Jon Wellinghoff from an agenda bent on promoting renewable energy and fighting climate change. Last fall, even as Congress dithered, FERC launched a landmark initiative that likely will lead to sweeping new rules for expanding the nation’s electric transmission grid, grounded on Wellinghoff’s belief in wind, solar, and green power resources.
People (November 2009)
Integrating New England Renewables
How to manage the green revolution.
Dramatic changes are coming to the electric industry, sparked by a surge of renewable energy and related transmission. Growth in demand-side resources, conservation and smart technologies will add integration dilemmas to an already complex power system.
Green Contracting
Structuring renewable agreements to survive change.
The potential for a federal renewable energy standard (RES) and carbon regulation, considered with the effect of state-imposed renewable energy standards, is fueling a strong, but challenging, market for renewable energy. Utilities are competing to sign up the best new projects, the types of renewable technologies available are increasing, and there are various government stimulus programs for energy; yet, the financial markets still are hesitant. Against this backdrop, how should contracts for power from new renewable resources be shaped so that those deals will look as good five, 10 and 15 years after execution as on the day the ink dries?
'T' Party Revolt
Transmission expansion costs are spread unevenly, driving a wedge between utilities and regions.
Back in June, the Bismarck Tribune ran an interview with North Dakota Public Service Commissioner Tony Clark that showed just how difficult it is to build national consensus for renewable energy.