Selling the Smart Grid - The Backlash
California learns painful lessons from its proposal to mandate demand response.
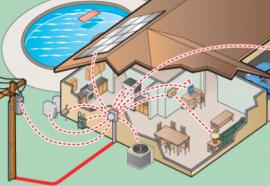
When the California Energy Commission (CEC) proposed to include programmable communicating thermostats in the state’s new building codes, it expected some push-back from home builders. It didn’t expect what it got: a major public outcry.